Remote working and employee mobility have become the norm. Companies need to ensure that their devices and data remain secure, wherever they are. This is one of the cornerstones of a company’s corporate IT security. Microsoft Intune responds to this need by offering a unified device and application management solution, directly from the cloud. In this article, we explain exactly what Microsoft Intune is, what it does (and doesn’t) do, and how best to use it.
What is Microsoft Intune?
Microsoft Intune is a solution for mobile device management (MDM) and mobile application management (MAM) solution. It enables companies to secure and manage mobile devices as well as Windows and macOS desktops via cloud policies, while protecting corporate data.
Intune integrates seamlessly with :
- Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure Active Directory), which manages identities and access, and enables conditional access policies to be applied for enhanced security.
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint for advanced threat protection, vulnerability management and automated remediation.
- Microsoft Endpoint Analytics to monitor device performance and identify problems that may affect the user experience…
- Microsoft Purview Information Protection for enterprise data protection with file encryption and classification.
- Windows Autopilot for automatic deployment and preconfiguration of new Windows devices.
It supports multiple platforms (Windows, macOS, iOS, Android) and enables consistent security policies to be applied.
Key features of Microsoft Intune
Microsoft Intune offers advanced features for managing and securing enterprise devices and applications.
Manage all your company’s devices
Do you need to manage and secure all your company’s devices, whether company-supplied or personal? With Intune, IT administrators can apply security policies and ensure that all devices comply with corporate standards.
Intune lets you manage and secure Windows, macOS, iOS and Android devices, whatever the platform.
IT administrators can :
Apply configuration and security policies (Wi-Fi, VPN, usage restrictions).
Restrict access to resources according to device status (e.g. conditional access via Entra ID).
Locate, lock or wipe a device. Completely erasing a compromised or lost device is called a Total Wipe.
💡Note: this feature is essential for companies that adopt “Bring Your Own Device”(BYOD) policies, where employees use their personal devices to access company resources.
Similarly, some employees use kiosks, industrial tablets or self-service PCs; Intune enables these devices to be configured and policies applied for their specific use.
IT administrators can :
Configure devices in kiosk mode for use limited to certain applications.
Manage shared devices with secure multi-user sessions.
Apply specific restrictions to field workers or industrial environments.
Manage mobile applications (MAM)
Do your employees use their own smartphones for work? With mobile application management, you can protect only business applications and data, without touching users’ personal data.
Intune makes it possible to secure and manage business applications without requiring full device registration.
IT administrators can :
Apply usage restrictions (e.g. no copying and pasting between a business app and a personal app).
Imposeauthentication and access protection rules.
Selective Wipe : deletes only business data from an application without affecting personal data.
Protect data and manage access
Your company’s data must remain secure, no matter where it’s stored or used. Intune helps prevent data leakage and enforces strict security rules.
IT administrators can :
Require encryption of business data stored on devices.
Block certain functions.
Apply conditional access strategies in integration with Microsoft Entra ID.
Manage updates
An out-of-date device is a business risk! With Intune, you can ensure that all devices are up to date, and use analysis tools to identify performance problems before they become critical.
IT administrators can :
Deploy Windows, iOS and Android updates centrally to ensure device security and compliance.
Enforce compliance policies (such as requiring active antivirus, prohibiting obsolete OS versions).
Analyze device performance with Endpoint Analytics (identify latency problems, track updates).

Book a free Modern Workplace diagnostic
Are your IT tools really adapted to your needs? Take advantage of a free 30-minute diagnostic to assess your current infrastructure and identify opportunities for improvement.
The benefits of Microsoft Intune for your business
Simplify device management
From a single console, your IT teams can manage all the company’s devices, apply security rules, deploy applications and resolve problems remotely. There’s no need to intervene physically on each workstation.
Less physical intervention, less maintenance, less wasted time – it all adds up to greater efficiency. By automating device and application management, Intune enables IT teams to concentrate on higher value-added tasks.
Enhancing data security
Your company’s data is precious and needs to be kept under control. Intune lets you :
- prevent information leaks by blocking unsecured data transfers.
- impose strict rules, such as requiring devices to have active antivirus, blocking those without the latest updates or preventing access to corporate resources from a compromised phone.
Intune also helps you apply compliance policies across all devices, by enforcing
- data encryption,
- multi-factor authentication. To find out more, read our article on two-factor authentication.
- access management.
Flexibility and mobility
Work has changed: employees want to be able to use their own devices and work from anywhere. With Intune, they can access company resources from their smartphone or personal PC, without compromising security. Business data remains isolated from personal data.
An employee without access to the right tools is an employee stuck. With Intune, essential applications and resources are available as soon as an employee logs on, on any approved device.
How to deploy Microsoft Intune in 5 steps?
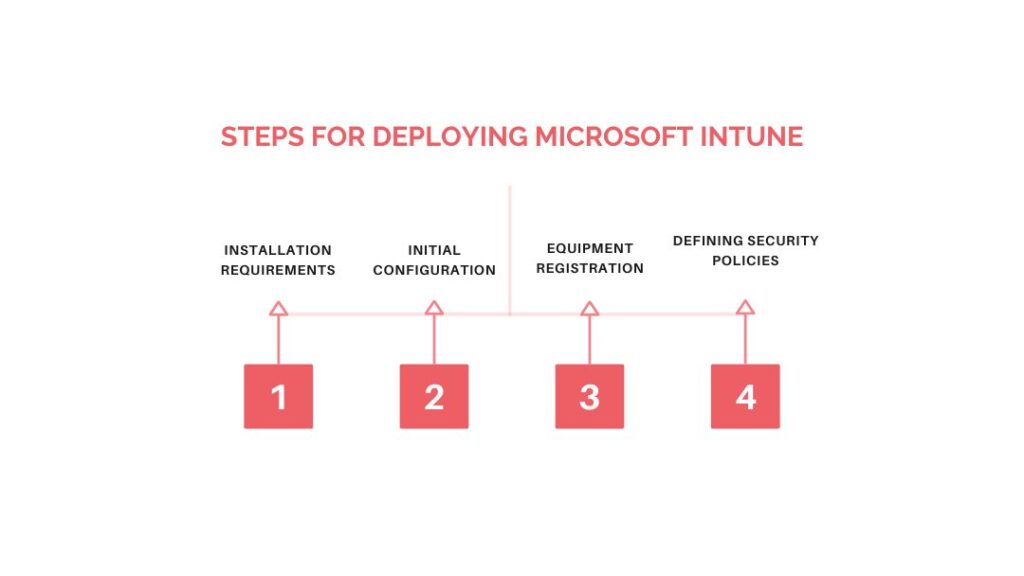
Step 1: Installation prerequisites
Before you start deploying Microsoft Intune, it’s essential to make sure your environment is ready. Check :
- Device compatibility: Intune supports Windows (10/11), macOS, iOS, Android. Check MDM management settings, as some devices require specific authorizations to be managed by Intune.
- License validity: Microsoft Intune is available as a standalone license. It is also included in several plans, including some Microsoft 365 plans (E5, E3, Business Premium F1, F3), Enterprise Mobility + Security plans such as E5, E3; and Microsoft 365 plans for public entities, such as G5, G3.
- That you have Microsoft Entra ID for authentication and identity management.
- Your IT administrators have the necessary authorizations.
Step 2: Configure Microsoft Entra ID
Access the Entra ID portal, then :
- Create user accounts manually in Microsoft Entra ID or synchronize them from a local directory with Microsoft Entra Connect. Make sure every user has an active Intune license to be managed.
- Create groups to organize users and devices
- Configure automatic device enrolment; for example, enable automatic MDM enrolment, authorize only corporate devices.
- Define security rules based on device status and user identity: require multi-factor authentication before accessing sensitive resources, block or restrict access to applications if a device is non-compliant (an obsolete OS, an unencrypted device…).
Step 3: Register devices
Once Microsoft Entra ID has been set up, the next step is to register the devices for management by Intune :
- Define the registration mode according to device type. For example, Fully Managed for business devices, Work Profile for BYOD, Kiosk Mode for dedicated terminals.
- Configure automatic registration with Windows Autopilot or Apple Business Manager.
- Provide your employees with a step-by-step guide to registering a device via the Intune Enterprise Portal.
Step 4: Deploy applications
Once devices have been registered with Intune, the next step is to distribute and manage business applications:
- Choose the types of applications to deploy.
- Define application deployment methods (mandatory or optional installation, use of MAM, definition of minimum version requirements).
- Monitor application deployment via the Intune console (successes, errors, failures).
Step 5: Apply security strategies
Once the applications have been installed, apply security strategies tailored to your needs:
- Define essential security policies (corporate data protection, device access management and compliance, secure network connections…).
- Apply policies according to device type: full management for corporate devices, or management limited to business applications and isolation of personal data for personal devices.
Automate device compliance.

Book a free Modern Workplace diagnostic
Are your IT tools really adapted to your needs? Take advantage of a free 30-minute diagnostic to assess your current infrastructure and identify opportunities for improvement.
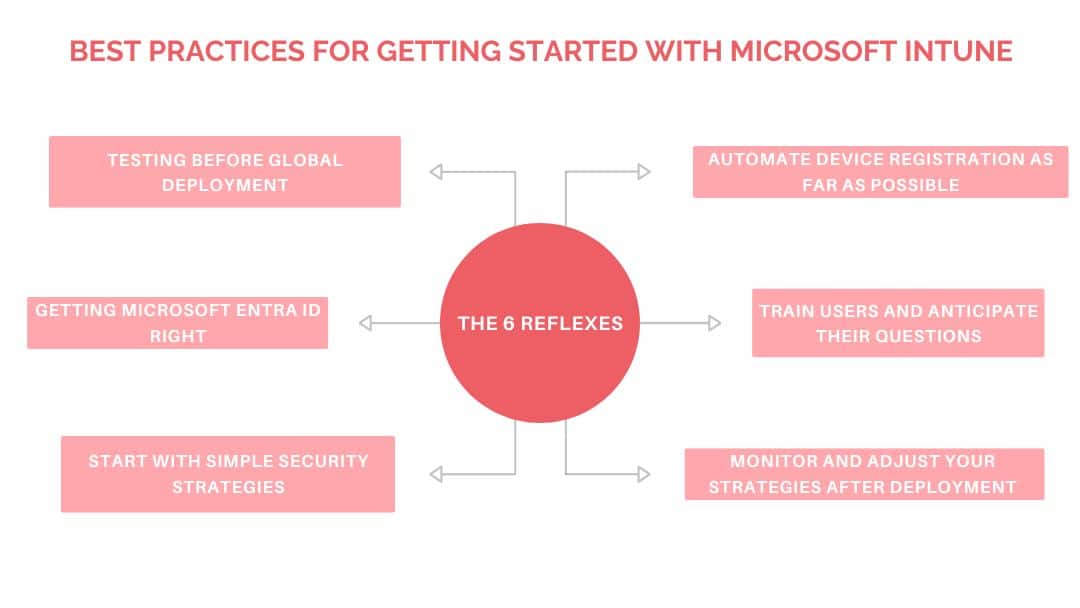
Best practices for getting started with Microsoft Intune
If you’re just getting started with Intune, there are a few best practices practices to follow.
Testing before global deployment
Intune is powerful, but the wrong configuration can block devices or cause access problems.
💡SmartYou tip: create a pilot environment with a small group of users to test registrations, application management and security strategies before extending it to the whole company.
Organizing Microsoft Entra ID
Intune really works in synergy with Microsoft Entra ID; if it’s poorly structured, you may find it hard to apply your strategies.
💡SmartYou tip: create dynamic groups to automatically classify devices and users according to their service, device type, and so on.
Start with simple security strategies
If you activate too many restrictions right from the start, you run the risk of blocking users and getting a flood of support requests. Start with simple rules, such as requiring a PIN, or enabling encryption, then fine-tune the settings over time.
Automate device registration wherever possible
Manual registration is error-prone and can be tedious for employees.
💡SmartYou tip: use Windows Autopilot, Apple Business Manager or Android Enterprise to automate registration and pre-configure devices before they reach users’ hands.
Train users and anticipate their questions
Successful Intune deployment also means well-trained, well-informed staff! Organize training sessions to introduce key Intune features and security best practices:
- Explain to employees what Intune does and doesn’t do (for example, “We don’t monitor your personal data”).
- Explain basic procedures, such as registering devices and using the Enterprise Portal application.
- Provide clear instructions on password management, multi-factor authentication and the importance of regular updates.
- Make sure users know how to report an incident quickly.
Finally, don’t neglect documentation: prepare practical guides, such as a registration guide or FAQ support, to reduce the number of IT tickets.
Monitor and adjust your strategies after deployment
The first few weeks after deployment are essential for identifying where adjustments need to be made. Use Endpoint Analytics to detect performance problems, and analyze Intune reports to see if certain rules are causing problems.
Common problems with Microsoft Intune
Here are the three most common problems we encounter.
Device does not register with Intune
When a device does not register correctly with Intune, it may be blocked or not detected by the administration console. As a result, the user cannot access company applications and resources. This can happen for a number of reasons. Here are the most frequent causes and the appropriate solutions.
| Possible problem | Solution |
| Device not compatible (OS too old, not supported) | Check that the device is running Windows 10/11, macOS, iOS or Android with a supported version. Update if necessary. |
| The user has the wrong permissions or no Intune license | Check in Microsoft Entra ID that the user has an Intune license and is part of a group authorized to register devices. |
| Automatic registration is incorrectly configured | Check registration settings in Windows Autopilot, Apple Business Manager or Android Enterprise. |
| Another MDM manager is active on the device | Check if another MDM is active. Remove old MDM management and check that the device is not locked by an old corporate policy. |
| Device blocked without explanation | Consult the error logs in the Microsoft Intune console (Endpoint Manager) to identify the cause of the problem. |
| Registration fails on a specific device | Test the registration on another device to see if the problem lies with the user or the device itself. |
Applications do not deploy correctly
Installations may fail, errors may appear, or certain applications may simply not be visible to users. The result: employees can’t access the tools they need. Here are the most common causes, and the appropriate solutions.
| Possible problem | Solution |
| The application is not compatible with the device | Check that the application is compatible with the OS and its technical prerequisites (e.g. minimum version required, specific dependencies). |
| The user does not see the application in the Enterprise Portal | Check that the application has been assigned to the user or group in Intune. Also check that the deployment mode is correct (mandatory or self-service). |
| Installation fails on some devices | Check installation logs in Intune and specific errors in Endpoint Manager (e.g. failure code 0x87D1041C for a rejected installation). Test installation manually on a device. Also check that the device has sufficient disk space. |
| Insufficient permissions to install the application | Check that the user has the necessary installation rights on the device. For Windows, it may be necessary to run the program in administrator mode. |
| The application is blocked by a security policy | Check whether a security restriction prevents installation (e.g. application not approved in a conditional access policy, blocking via a MAM/MDM rule, requirement for a signing certificate for internal applications). |
| Application too large for deployment mode | Some applications (particularly Win32) require deployment in Win32 App mode, with a suitable deployment container. Also check that the device has enough free disk space. |
A device is marked “non-compliant” even though it meets all requirements
Here are the most common causes and the appropriate solutions.
| Possible problem | Solution |
| Compliance rules are too strict | Check and adjust Intune compliance policies (e.g. OS version requirements, encryption enabled, antivirus installed). Relax certain rules if necessary. |
| The device has not yet been evaluated by Intune | Force manual synchronization from the Intune Enterprise Portal or Microsoft Endpoint Manager console. Compliance may sometimes require an automatic assessment cycle that takes a few minutes. |
| The user did not restart his device after an update | Ask the user to restart the device and reconnect the account. Check that the device is on a corporate network and that certificates are up to date. |
| Antivirus or encryption not detected correctly | Check in Intune whether antivirus or encryption is recognized. If not, force a policy update and reassess compliance. |
| A conditional access problem blocks the device | Check Conditional Access rules in Microsoft Entra ID. Test by temporarily excluding the user or device, but only in a controlled setting to avoid a security risk. |
| Device offline or unable to synchronize policies | Check that the device has an Internet connection and can contact Microsoft servers. Try connecting to a different network. |
How SmartYou helps you use Microsoft Intune
SmartYou is your Microsoft partner and offers comprehensive support to help you make the most of Microsoft Intune, ensuring that your business benefits from optimal device management and enhanced security. Our team of experts will guide you through every step of the process.
We start witha thorough analysis of your specific device management and securityneeds. This enables us to design a customized solution that aligns with your business objectives.
Our experts take care of installing and configuring Microsoft Intune, and ensure seamless integration with your existing infrastructure.
SmartYou offers customized training sessions for your IT teams and end-users, to help them fully master Intune’s functionalities. Our support service is available to quickly resolve any technical issues or questions.
By listening to your needs, we regularly adjust and optimize your Intune configurations to ensure your business benefits from the latest innovations and remains protected against emerging threats.
With SmartYou, your company can exploit the full potential of Microsoft Intune to improve device management and strengthen IT security.
In conclusion, Microsoft Intune is a powerful solution for managing devices and applications within the enterprise. By following best practices, such as establishing security policies and training users, companies can maximize the benefits of Intune. To find out more about how to optimize your digital environment, discover our Modern Workplace service, which helps you integrate and optimize modern IT solutions.
Any questions?
How do I get Microsoft Intune?
Just three steps:
- Buy a license: Intune is included in several subscriptions or available as a standalone license.
- Subscribe via the Microsoft portal, log in with an administrator account, and under Billing > Buy services, search for “Microsoft Intune”.
- Activate Intune in Microsoft Entra ID.
What license do I need to use Intune?
To use Microsoft Intune, you need an appropriate license. Intune is included in several Microsoft licensing packages, including .
- Microsoft 365: E5, E3, Business Premium, F1, F3
- Enterprise Mobility + Security (EMS): E5, E3
- Microsoft 365 for public entities: G5, G3
- Microsoft 365 Education A5 and A3
If you don’t have one of these licenses, you can purchase a stand-alone Intune license. See Microsoft prices.
What is the Microsoft Intune suite?
Microsoft Intune is not a “suite” in the strict sense of the word, but a cloud service for managing mobile devices and applications (MDM/MAM).
However, Microsoft now offers Microsoft Intune Suite, a complementary offering that adds advanced features to Intune, including :
- Microsoft Intune remote help
- Endpoint Privilege Management
- Advanced Analytics
- Enterprise Application Management
- Microsoft Cloud PKI
- Microsoft Intune Plan 2 (included in the suite, but also available as an add-on to Intune Plan 1).
How do I register a device with Intune?
Here are the simple steps for registering a device, depending on its type.
Windows (PC & Tablets)
The most common method is to register via Windows settings:
- Open Windows Settings → Accounts → Professional Access.
- Click on “Login”, enter your professional e-mail address.
- Follow the instructions to complete registration.
If your company uses Windows Autopilot, registration is automatic on first startup. If IT has enabled automatic Intune registration via Microsoft Entra ID, the device will be managed directly after the account has been added.
macOS (MacBook, iMac)
- Download the Enterprise Portal app from the App Store.
- Open the app and log in with your business account.
- Follow the registration steps to register your device.
- Accept MDM profile in macOS settings to finalize registration.
If your company uses Apple Business Manager, registration is automatic.
iOS / iPadOS (iPhone, iPad)
- Go to the App Store and download “Intune Enterprise Portal”.
- Open the app and log in with your business account.
- Follow the instructions to complete registration.
- Accept MDM profile in device settings.
If your company uses Apple Business Manager, registration can be automatic.
Android
Case 1: Personal device
- Download the “Intune Enterprise Portal” app from the Play Store.
- Log in with your professional account.
- Accept the creation of a “professional profile” that isolates professional data from personal data.
Case 2: Company-supplied device. Registration takes place on the first start-up of the device, either automatically via Android Zero-Touch Enrollment, by scanning a QR Code, or by entering a provisioning code provided by IT.
Is Intune better than SCCM?
Firstly, it’s no longer correct to speak of “SCCM” (System Center Configuration Manager): it has been renamed “Microsoft Configuration Manager”.
Secondly, it’s not a question of “best”, but rather of appropriate use. Microsoft Intune and Microsoft Configuration Manager are designed for different needs, and in some cases, they can be complementary.
| Criteria | Microsoft Intune | Microsoft Configuration Manager |
| Management type | Cloud-first | Mainly on-premise, but can manage remote devices with a Cloud Management Gateway (CMG) |
| Managed devices | Windows, macOS, iOS, Android | Mainly Windows (can handle Linux/macOS, but limited) |
| Deploying updates | Directs devices to Windows Update for Business, without granular control | Uses WSUS + SUP for advanced update control |
| Application deployment | Microsoft Store, MSI, Win32 (EXE with limitations), mobile apps | MSI, EXE, PowerShell scripts + system image deployment |
| Safety and compliance | Conditional access, security policy management, Entra ID integration | Granular configuration and patch control |
| Complexity | Easier, quicker set-up | More complex, requires dedicated infrastructure |
| Ideal use case | Cloud-first businesses, mobile device management (BYOD, teleworking) | Large companies with secure internal networks, need advanced Windows control |
| Hybrid mode possible? | Yes, co-managed with SCCM | Yes, via co-management with Intune or tenant attach for centralized management |
Verdict: Intune or Microsoft Configuration Manager If your business is cloud- and telecommuting-oriented, go for Microsoft Intune.
If you manage a Windows estate in a secure on-premise environment, go for Microsoft Configuration Manager.
If you want the best of both worlds, consider co-management with Intune and Microsoft Configuration Manager.





