OneDrive is much more than just an online storage space. It’s a powerful tool that makes it easy to collaborate, save and share files. But behind this apparent ease lies a far more complex reality: the security of your data. Who has access to your files? How do you protect your sensitive information? What happens in the event of a bug or block? What’s the difference between a personal account and a corporate account? SmartYou answers all these questions.
Which solution should you choose for your business: Office 365 or Microsoft 365?
Our practical guide, created by our experts, offers you a detailed comparison of the two solutions.
What is OneDrive?
OneDrive is an online file storage and synchronization service offered by Microsoft. It is integrated into the Microsoft 365 suite and accessible via a dedicated application or web browser. The service enables users to store files in the cloud, synchronize them between different devices (computers, smartphones, tablets) and access them at any time, as long as they have an Internet connection.
OneDrive supports online collaboration, including real-time document co-editing, especially with Microsoft applications such as Word, Excel and PowerPoint.
There are two main versions: OneDrive Personal, for individual use, and OneDrive Enterprise, which is more closely integrated with SharePoint and Microsoft Teams.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of OneDrive?
Benefits
OneDrive offers several key advantages:
- Excellent integration with Microsoft 365 suite tools.
- Automatic synchronization between the user’s various devices.
- Automatic backup of system folders and restore options.
- Granular control of file shares.
Disadvantages
Despite its strengths, OneDrive has certain limitations:
- Microsoft servers are located outside the user’s country of origin. This can raise questions about compliance (DPA, digital sovereignty) and the confidentiality of sensitive data.
- Many advanced functions (co-editing, sharing, real-time backup) require a stable Internet connection.
- In a professional context, fine-tuning security settings, access rights and compliance rules (especially with Microsoft Purview or Intune) can be complex.
- The default storage space available for each OneDrive user is just 1TB. You can increase this to 5TB if your company has an eligible subscription (Microsoft 365 E3/E5, Office 365 E3/E5).
If you’re still undecided between Microsoft’s two leading solutions, Sharepoint and OneDrive, read our comparison article: How do I choose between Sharepoint and OneDrive?

Book a free Modern Workplace diagnostic
Are your IT tools really adapted to your needs? Take advantage of a free 30-minute diagnostic to assess your current infrastructure and identify opportunities for improvement.
How do you protect your data on Onedrive?
For individual users (OneDrive Personal)
The options are more limited than in the professional versions, but it is possible to optimize security:
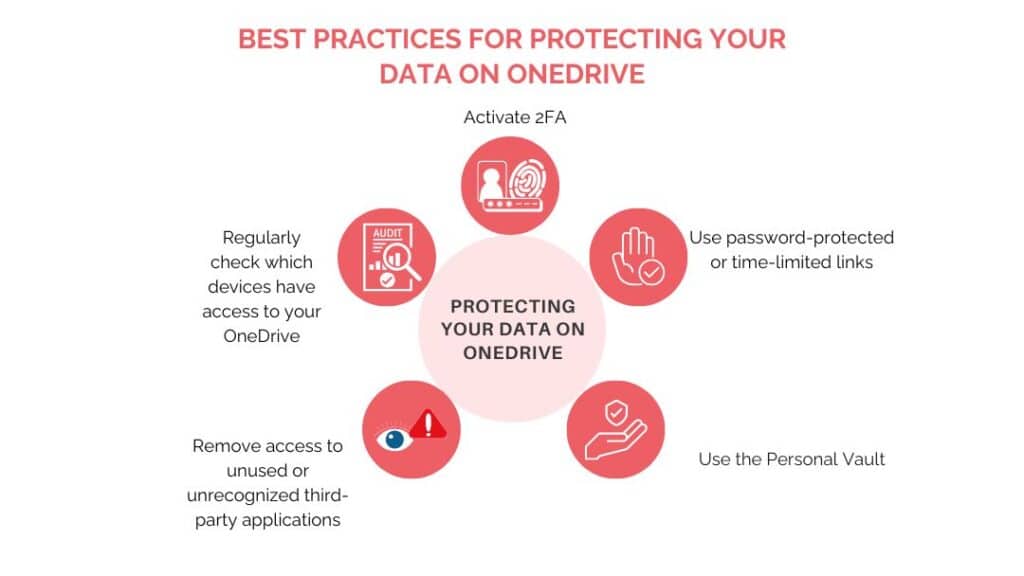
- Activate two-step verification (2FA) to protect access to your account.
- Use the Personal Vault to protect sensitive files with enhanced security.
- Regularly review the devices that have access to your OneDrive and revoke those that are no longer in use.
- Use password-protected or time-limited links to share files. Avoid links that are open to everyone.
- Remove access to unused or unrecognized third-party applications from your Microsoft account.
For businesses (OneDrive Enterprise / Microsoft 365)
The above advice remains valid for enterprise users, but implementation varies: security features are usually integrated into an overall strategy, with tools such as Microsoft Intune, Azure AD, Microsoft Purview or Defender for Cloud Apps. Users have to follow instructions rather than change settings themselves. Here’s a clear comparison:
| Board | Individuals (OneDrive Personal) | Enterprise (OneDrive Enterprise) | Remarks |
| Two-factor authentication (2FA) | Yes | Yes | Often mandatory for enterprises (via Azure AD) |
| Use reinforced storage space | Yes (Personal safe) | No | Replaced by centralized mechanisms (DLP, encryption, labels) |
| Controlling connected devices | Yes | Partially | Often automated via Intune (MDM) |
| Checking shared files | Yes | Yes | Possible restrictions defined by the organization |
| Removing third-party applications | Yes | Rarely | Access often managed by administrators |
| Automatic folder backup | Yes | Variable | Managed or restricted according to the organization’s strategy |
So who does what?
IT administrators :
- Use Azure Active Directory to apply MFA to all accounts.
- Define conditional access rules, for example restricting access according to location, device type, or level of risk detected.
- Enable Data Loss Prevention (DLP) with Microsoft Purview to automatically detect and block sensitive data
- Use confidentiality labels to automatically apply protection rules to documents.
- Enable advanced auditing in the Microsoft Compliance Center to monitor critical actions.
- Manage sharing outside the organization.
- Manage devices via Microsoft Intune.
- Configure file recovery mechanisms.
Professional users :
- Respect internal security policies
- Avoid storing confidential data outside designated areas
- Do not change the configuration of OneDrive on a business device without approval from the IT team.

Which solution should you choose for your business: Office 365 or Microsoft 365?
Our practical guide, created by our experts, offers you a detailed comparison of the two solutions.
What are OneDrive’s data security features?
What security guarantees does Microsoft offer?
Microsoft implements security measures that focus on several areas:
- Microsoft engineers do not have access to user files, except in the event of an intervention. In this case, rights are temporary and limited (principle of least privilege).
- Files are encrypted in transit (via TLS) and at rest (via AES256), with enhanced key management via Azure Key Vault.
- OneDrive detects suspicious connections, sends e-mail alerts and automatically blocks certain abnormal activities.
- In the event of accidental deletion, corruption or ransomware attack, users can restore their files or their entire OneDrive within 30 days (for Microsoft 365 subscriptions only).
- Downloaded files are scanned for known threats.
💡These measures do not exempt users from configuring their settings correctly, nor companies from implementing appropriate internal policies.
Security comparison: OneDrive Personal vs. OneDrive Enterprise
Security in OneDrive Personal and OneDrive Enterprise is based on very different principles, in terms of control, architecture and responsibility.
Here’s a detailed comparison.
| Criteria | OneDrive Personal | OneDrive Enterprise (Microsoft 365) |
| Account type | Individual user | Professional or school account managed by an organization |
| Responsibility for safety | Users configure and manage their own settings | The organization (CIO, IT administrators) defines global policies |
| Multi-factor authentication (2FA) | Optional (to be activated via Microsoft account) | Recommended or required via Azure AD |
| Access control | Basic: login via Microsoft IDs | Advanced: conditional access according to device, location, risk level |
| PersonalVault | Yes | No |
| Data encryption | Yes – automatic on server side (TLS in transit, AES at rest) | Yes – ditto, but can be strengthened (encryption with client keys, AIP) |
| Device management | Manual (via Microsoft account) | Centralized (via Microsoft Intune or other MDM/EMM) |
| File sharing | Basic control: read/modify, duration, password | Granular control: restrictions by user, domain, file type |
| Version history | Yes – available for Office files | Yes – with configurable retention (and integrated into compliance strategies) |
| Incident recovery (e.g. ransomware) | Can be restored via “OneDrive Restore”. | Yes – advanced restoration + audit logs and security alerts |
| Data loss prevention (DLP) | Not available | Yes – via Microsoft Purview |
| Labelling and classification | Not available | Yes – via Sensitivity Labels (Microsoft Purview Information Protection) |
| Monitoring and auditing | No | Yes – via Audit Log, Microsoft Defender, etc. |
| Remote data deletion | No | Yes – via Intune (selective or complete wipe) |
| Compliance and regulations | No contractual guarantee (depends on consumer cloud) | Centralized compliance management (e.g. RGPD, ISO 27001, etc.) |
How do I secure a file in OneDrive?
A non-shared file is private by default, as long as it has not been placed in a shared folder or any authorization has not been modified. This means that protection measures are not the same whether the file is shared or not.
Securing a private file
Here’s how to strengthen your security:
- Protect your Microsoft account by activating two-step verification.
- Use the Personal Vault.
- Enable device encryption to protect your files in the event of loss or theft of a locally synchronized device:
-On cell phones (iOS/Android), encryption is generally enabled by default if a lock code is set.
-On computers (Windows/macOS), it can be activated manually via BitLocker or FileVault, but is not always available depending on the system edition.
- Avoid automatically synchronizing sensitive folders on a shared device.
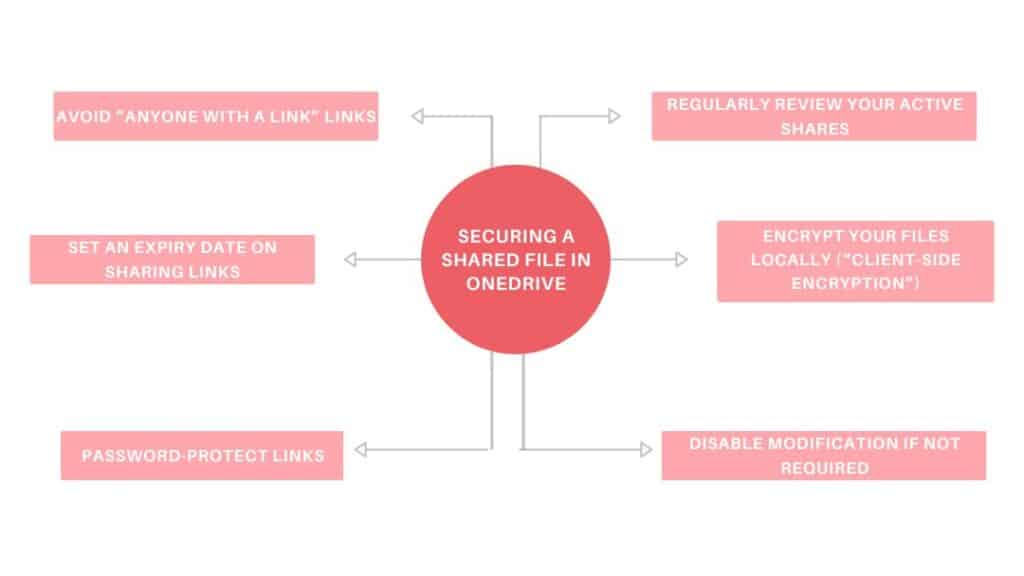
Securing a shared file
Unquestionably, the most frequent usage errors concern sharing. Here are a few common examples:
- The user thinks he’s shared a file with just one person, when in fact anyone who owns the link can access it.
- A sharing link remains active for months, without expiry.
- A confidential file is put in a shared folder by mistake.
As soon as you share a file, even with just one person, you create a risk of exposure. Here’s how to limit that risk:
First of all, only share files with identified persons. Avoid “anyone who has the link” links. Prefer direct e-mail sharing, with authentication required.
Next, set an expiry date on the sharing links, which prevents access beyond a defined period. You can also password-protect links.
Regularly review your active shares. From the OneDrive online interface, view shared items and delete those that are no longer necessary or sensitive.
Encrypt your files locally (“client-side encryption”) with a tool like 7-Zip or BitLocker (Windows Pro), if you don’t want to take any risks. This only applies to files you’ve encrypted manually before uploading them to OneDrive.
Finally, disable modification if you don’t need to: when sending a document, a read-only link is more secure than an editable one.
💡Note: all these features are available with a paid Microsoft 365 subscription. However, the expiration date for sharing links and password protection of links are not available with the free version of OneDrive. In a professional context, certain options can also be activated or restricted by the organization’s administrator.
In terms of sharing and security settings (password, expiration, rights), folders and files are treated in almost identical fashion. On the other hand, specific functionalities (safe, history, individual encryption) only apply to files.

Book a free Modern Workplace diagnostic
Are your IT tools really adapted to your needs? Take advantage of a free 30-minute diagnostic to assess your current infrastructure and identify opportunities for improvement.
How does the Personal Vault work in OneDrive?
What is the Personal Vault?
The Personal Vault is a location within OneDrive Personal with added security. It is designed for storing sensitive files (passports, identity cards, contracts, etc.).
Here are its main features:
- Access protected by a second factor (SMS code, fingerprint, facial recognition, PIN code, etc.).
- Automatic lock after a period of inactivity (default 20 minutes).
- Microsoft server-side encryption, as for the rest of OneDrive, but with reinforced access control.
💡Good to know:
- On free accounts, the number of files in the safe is limited to 3.
- On paid Microsoft 365 accounts, there is no limit to the number of files in the safe.
- The Personal Vault does not exist in OneDrive Enterprise.
- It is available on OneDrive Web, the mobile application (Android/iOS) and the OneDrive for Windows application. It is not accessible from macOS.
The various Personal Vault blocks
Locking when safe is opened
The user is logged into his OneDrive account, but cannot unlock the Personal Vault.
Probable cause: a temporary problem at Microsoft.
Access blocking by medium or browser
The safe is accessible on mobile, but not on PC; or works on Edge but not on Firefox.
Probable cause: temporary compatibility problem, corrupted cache or cookies, or restrictions depending on configuration.
Personal Vault does not appear at all
The Personal Vault icon or option cannot be found.
Possible causes:
- The user is on OneDrive Enterprise (Personal Vault does not exist in this version).
- The user has a free Microsoft account and has already reached the limit of 3 files allowed in the safe.
- The device used is not compatible (e.g. on macOS).
The safe opens, but some files are inaccessible or corrupted
Possible causes:
- Damaged files.
- Synchronization interrupted or incomplete.
- Network connection error when downloading or opening.
Microsoft account blocking
Unable to access the safe because the user has lost access to their Microsoft account (account locked, 2FA lost, etc.).
In this case, follow the official account recovery procedure at account.live.com/password/reset.
What should I do if the Personal Vault is blocked?
The troubleshooting procedure targets the most common blockage, i.e. the inability to access the Personal Vault even though the OneDrive account is working normally.
- Check your general access to OneDrive: if you can’t access OneDrive at all, start by recovering access to your Microsoft account (https://account.live.com/password/reset).
- Try another medium. Try the OneDrive application on Windows, the OneDrive mobile application (iOS/Android), or another browser.
- Make sure you’re using a compatible device (the Personal Vault is not accessible in the OneDrive application on macOS).
- If you’re on a free account, check that you haven’t already reached the limit of 3 files in the safe.
- If you’re using a web browser, clear the cache and log in again. On browser: delete cache and cookies. Log out of OneDrive, then log back in.
- If several users report the same problem, it’s likely that the bug comes from Microsoft. Check the Microsoft forum or the service status to verify.
- If the problem persists, open a support ticket via the OneDrive application or the Microsoft portal.
Who can access my OneDrive?
In the case of OneDrive Personal, it’s very simple: only the Microsoft account holder has the access credentials (email + password + 2FA) to access the whole of OneDrive.
It can also share a file or folder, via a link or an e-mail invitation. Anyone who has the link, or who has been invited, can access it according to the rights defined (read-only, modification). However, if you use a “anyone with the link” link, access does not require authentication.
But how does this work within the company?
It’s important to understand that OneDrive Enterprise is linked to a business (or school) account, managed by an organization. This means that stored files are not “private” in the personal sense: they belong to the organization, even though the user may have day-to-day control over them.
Consequently, administrators can access OneDrive Enterprise within the framework of the management rights assigned by the organization, and always in compliance with laws and internal company policies, to :
- Assign access (e.g. delegate temporary access to another employee),
- View or restore files,
- Analyze content (via DLP rules, privacy labeling),
- Access audit logs and action history.
💡In Switzerland, the protection of employee privacy is guaranteed by Article 328b of the Swiss Code of Obligations. However, employers may access data stored on company systems if justified by a legitimate reason, such as suspicion of abuse, prolonged absence or departure, or for reasons of IT security.
Our advice: for your strictly private files, use a storage space independent of the company’s (e.g. OneDrive Personal, external hard drive or private cloud service).
Secure your company’s OneDrive with SmartYou
SmartYou is the ideal partner for securing your company’s OneDrive. With over 20 years’ expertise and a focus on efficiency and security, SmartYou offers customized solutions to meet the specific requirements of your work environment.
We understand the importance of maintaining a secure level of access while optimizing productivity. Our services include Microsoft 365 management and oversight, harmonization of your IT processes, and expert management of associated tools such as Intune and Autopilot. Our team is committed to providing a robust and reliable infrastructure, ensuring your data is protected from digital threats.
We invite you to discover how we can transform your digital workspace into a secure fortress, while facilitating seamless collaboration. Visit our Modern Workspace services to find out more.
In conclusion, data security on OneDrive is paramount for any business. By adopting good practices and using the right tools, such as those offered by Smart You, you can strengthen your data security and optimize your digital working environment with confidence.